
Thoracoscopy
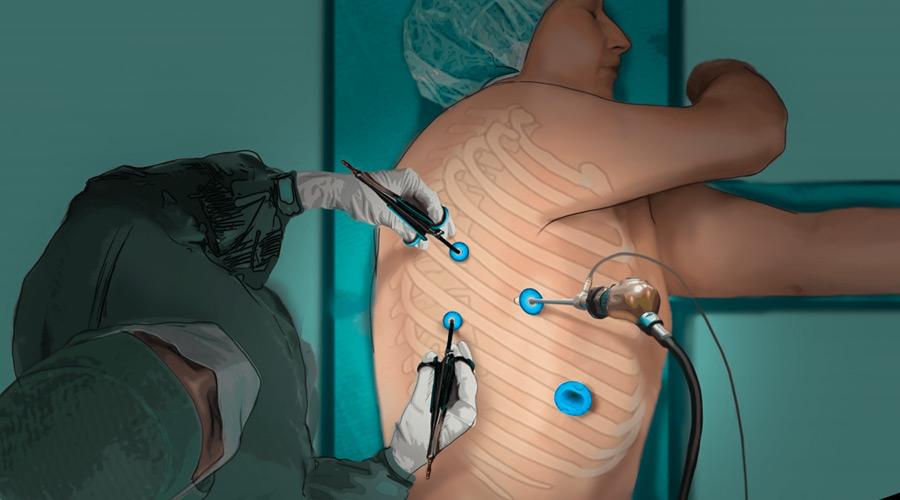
Thoracoscopy
Thoracoscopy, also known as video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS), is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to examine and treat conditions within the chest cavity, specifically the pleural space (the area between the lungs and the chest wall) and the structures within it. Thoracoscopy involves the use of a thoracoscope, a thin, lighted tube with a camera, and specialized surgical instruments. This procedure can be both diagnostic and therapeutic.
Here are some key aspects of thoracoscopy:
Purposes of Thoracoscopy:
-
Diagnostic Thoracoscopy: It is used to investigate the cause of unexplained chest symptoms or to obtain tissue samples (biopsies) for laboratory testing to diagnose conditions such as:
- Pleural effusion (accumulation of fluid in the pleural space).
- Lung nodules or masses.
- Infections within the chest cavity.
- Pleural thickening or pleuritis.
- Unexplained chest pain or discomfort.
-
Therapeutic Thoracoscopy: In addition to diagnosis, thoracoscopy can be used to treat various conditions, including:
- Drainage and removal of pleural effusions.
- Removal of blood clots or debris from the pleural space.
- Pleurodesis: A procedure to fuse the two layers of the pleura (the membranes lining the chest cavity and lungs) to prevent recurrent pleural effusions.
- Lung biopsy or wedge resection for the removal of small lung nodules or localized lung diseases.
- Treatment of certain conditions like empyema (pus in the pleural space).
Procedure:
During a thoracoscopy procedure:
- The patient is usually placed under general anesthesia or sometimes local anesthesia with sedation.
- One or more small incisions (usually 1-2 cm in length) are made between the ribs on the affected side.
- The thoracoscope, with a camera and light source, is inserted through one incision, and surgical instruments are introduced through the other incisions.
- The surgeon can visualize the inside of the chest cavity on a video monitor and perform the necessary diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
- Once the procedure is complete, any instruments and the thoracoscope are removed, and the incisions are closed with sutures or staples.
Recovery:
Recovery from thoracoscopy is generally quicker and less painful than traditional open chest surgery because it is minimally invasive. Most patients spend a shorter time in the hospital and experience less postoperative pain and scarring. The specific recovery period can vary depending on the procedure's purpose and the patient's overall health.
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with thoracoscopy, which should be discussed with the surgeon before the procedure. Thoracoscopy is performed by thoracic surgeons or other specialized surgeons with expertise in minimally invasive techniques and is a valuable approach for both diagnosis and treatment of chest and lung conditions.