
Pulmonary Function Test (PFT)
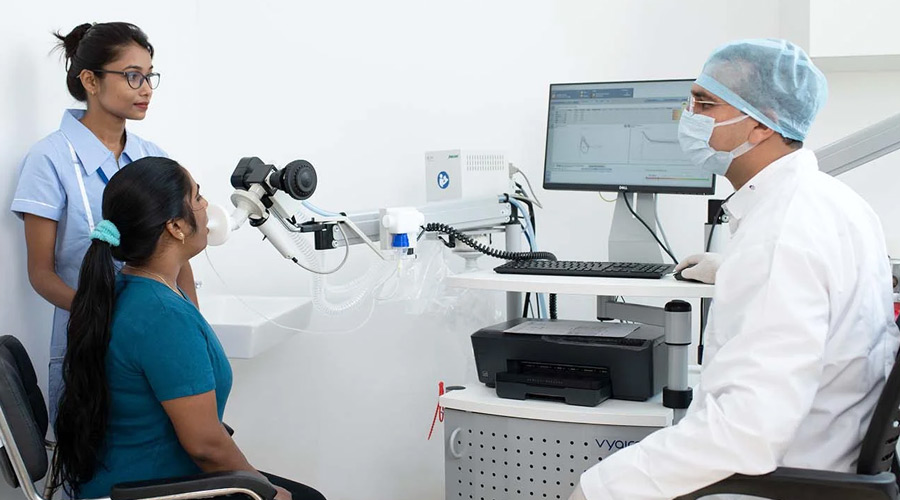
Pulmonary Function Test (PFT)
A Pulmonary Function Test (PFT) is a group of non-invasive diagnostic tests that assess how well your lungs are functioning. These tests are valuable in diagnosing and monitoring various lung conditions and can help healthcare professionals understand the mechanics of your breathing. PFTs are often performed by pulmonologists, respiratory therapists, or other trained healthcare providers.
Here are the primary components and purposes of PFTs:
-
Spirometry: Spirometry is the most common PFT and measures lung function by assessing the amount of air you can inhale and exhale and how quickly you can do so. During spirometry, you will breathe into a machine called a spirometer. Key measurements include:
- Forced Vital Capacity (FVC): The maximum volume of air you can forcefully exhale after taking a deep breath.
- Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 second (FEV1): The volume of air you can forcefully exhale in the first second of exhalation.
- FEV1/FVC ratio: A comparison of FEV1 to FVC, which helps diagnose obstructive lung diseases like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
-
Lung Volume Measurement: These tests measure the volume of air in the lungs and can help diagnose restrictive lung diseases, which affect lung expansion. Examples include:
- Total Lung Capacity (TLC): The maximum volume of air your lungs can hold.
- Residual Volume (RV): The amount of air that remains in the lungs after a complete exhalation.
-
Diffusion Capacity: This test measures the ability of the lungs to transfer oxygen from the air sacs into the bloodstream. It can help diagnose conditions that affect gas exchange, such as interstitial lung disease.
-
Bronchodilator Response: After baseline spirometry, you may be given a bronchodilator (a medication that opens airways), and then spirometry is repeated to see if there is an improvement in lung function. This can help diagnose and assess the reversibility of airway obstruction, such as in asthma.
-
Methacholine Challenge Test: This test is used to diagnose bronchial hyperreactivity, which is often seen in asthma. You inhale increasing concentrations of a substance called methacholine, which can provoke bronchospasm in individuals with sensitive airways.
PFTs are useful for diagnosing a range of lung conditions, including asthma, COPD, pulmonary fibrosis, bronchiectasis, and other restrictive or obstructive lung diseases. They are also valuable for assessing the severity of lung disease, monitoring disease progression, and evaluating the effectiveness of treatment.
It's essential to follow any preparation instructions provided by your healthcare provider before undergoing PFTs, as factors like avoiding certain medications or not smoking before the test can impact the results. After the tests, your healthcare provider will interpret the results and discuss them with you to formulate an appropriate treatment plan or determine the need for further evaluation.